GW-FEAST: Difference between revisions
Lorikrammer (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Lorikrammer (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
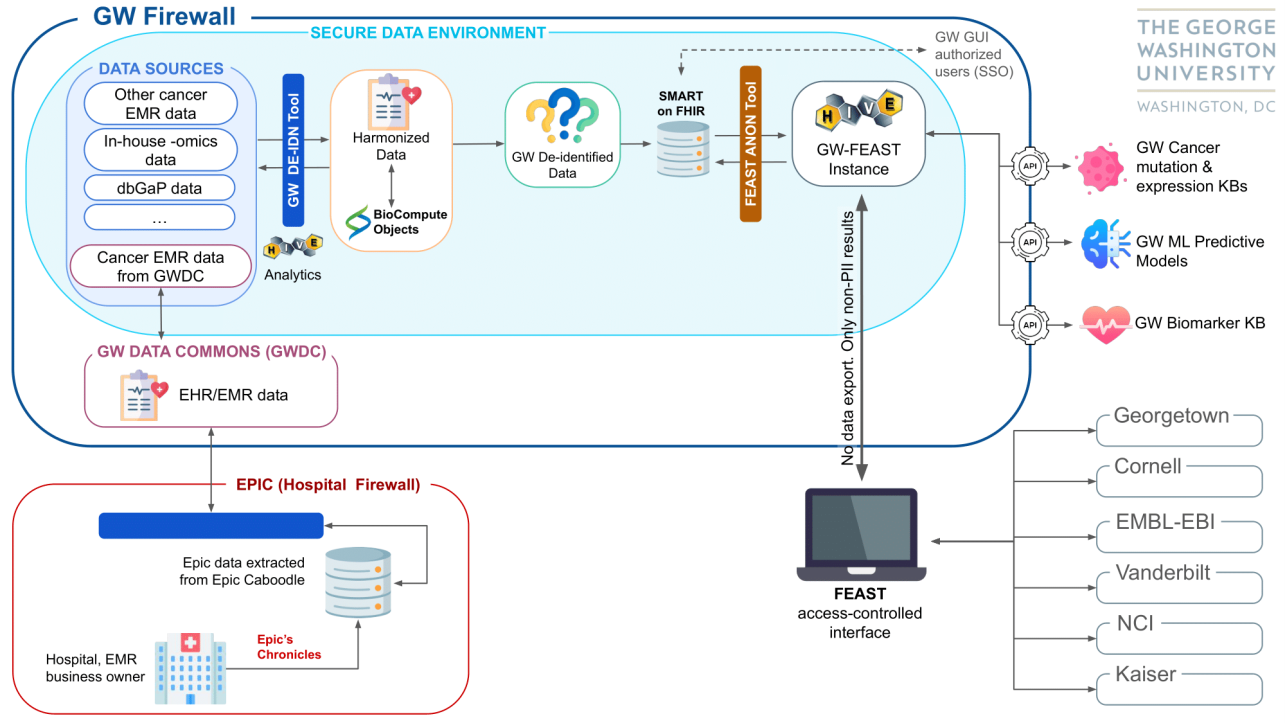
Federated Ecosystems for Analytics and Standardized Technologies (FEAST) is a cloud-based, agile bioinformatics and data analysis platform under development through the ARPA-H Biomedical Data Fabric (BDF) toolbox program. The project is led by [https://dnahive.com DNA-HIVE] and other funded collaborators include Cornell University, Vanderbilt University, Georgetown University, European Bioinformatic Institute, and Kaiser Permanente. Our team is responsible for the GW instance of FEAST (GW-FEAST) and for co-leading the project with DNA-HIVE. This project is part of the ARPA-H FEAST performer team initiative to create bridges across data silos and make health data more accessible and usable. | |||
Several hospitals and cancer centers will have a FEAST platform, which enables cross-site data analysis without the need to export or transform the data. Currently, large chunks of data are used by insurance companies, pharmaceutical companies, and others for research and development purposes. The FEAST platform, which is particularly strong with noisy, real-world data, aims to enable more precise data selection for research use while preserving patient privacy. When clinical data is submitted to the suite of tools, submission is handled via the HL7 FHIR protocol, ensuring only authorized parties ever have access to protected data. Models that provide update mechanisms such as online training will be updated appropriately without retaining any personally identifiable information (PII). Thus, these tools support federated data sets and training without ever retaining clinical PII within the system. All services are treated as independent microservices through containerization within docker containers. | |||
==== GW-FEAST Project Architecture ==== | |||
[[File:GW-FEAST Architecture.png|thumb|1285x1285px]] | |||
Revision as of 16:40, 13 December 2024
Federated Ecosystems for Analytics and Standardized Technologies (FEAST) is a cloud-based, agile bioinformatics and data analysis platform under development through the ARPA-H Biomedical Data Fabric (BDF) toolbox program. The project is led by DNA-HIVE and other funded collaborators include Cornell University, Vanderbilt University, Georgetown University, European Bioinformatic Institute, and Kaiser Permanente. Our team is responsible for the GW instance of FEAST (GW-FEAST) and for co-leading the project with DNA-HIVE. This project is part of the ARPA-H FEAST performer team initiative to create bridges across data silos and make health data more accessible and usable.
Several hospitals and cancer centers will have a FEAST platform, which enables cross-site data analysis without the need to export or transform the data. Currently, large chunks of data are used by insurance companies, pharmaceutical companies, and others for research and development purposes. The FEAST platform, which is particularly strong with noisy, real-world data, aims to enable more precise data selection for research use while preserving patient privacy. When clinical data is submitted to the suite of tools, submission is handled via the HL7 FHIR protocol, ensuring only authorized parties ever have access to protected data. Models that provide update mechanisms such as online training will be updated appropriately without retaining any personally identifiable information (PII). Thus, these tools support federated data sets and training without ever retaining clinical PII within the system. All services are treated as independent microservices through containerization within docker containers.
GW-FEAST Project Architecture